
Here is the unfortunate reality. Along with things that make our lives easier — like the development of technology and network infrastructures — we’ve also seen a dramatic increase in cyber crimes, network breaches, and system corruption.
That means the need for tech skills — and cybersecurity engineers — to combat these new and growing problems.
Why is cybersecurity engineering important?
When the COVID-19 pandemic hit, many businesses were not equipped or ready to work remotely. Similarly, government agencies were overwhelmed by the significant amount of people who needed federal and state support after losing their jobs or falling ill.
According to Cisco’s 2021 Cybersecurity Report, “cyber threats impact our lives on a human level – from threats against our democracy, to our health care, to the organizations we work within.”
The strain on these systems has highlighted some serious issues that may need to be addressed by government policy. One of those issues was the future of cybersecurity.
According to a research report published by Atlas VPN, the cost of cybercrime equaled 1% of the global GDP in 2020, easily exceeding $1 trillion. Cybersecurity spending alone accounted for $145 billion, which was 50% higher than global spending in 2018.
What is a cybersecurity engineer?
In short, cybersecurity engineering is the protection of data systems. A cybersecurity engineer is the person who does this job, and oversees and protects the network.
Cybersecurity engineers work to identify gaps across the network, develop solutions to protect the network, and control who can access the network data.
But the heart of what they do is to keep companies safe so they can run efficient businesses. As we become more dependent on technology, cyber attacks continue to rise, especially ransomware attacks. A cybersecurity engineer can work hard to prevent these attacks from ever happening and create a mitigation plan when issues do arise.
Become a cybersecurity engineer and you could make these attacks a thing of the past, protecting your company’s valuable assets, in turn, becoming an asset yourself.
What does a cybersecurity engineer do?
In general, cybersecurity engineers overlook a company’s network infrastructure as well as all devices, services, and assets in the IoT. They are the core player throughout the entire workflow lifecycle, from planning to reporting and optimizing.
The most significant threats against network security include:
- Threats created with remote working
- Securing Internet of Things (IoT) such as smart home devices and security systems
- New types of ransomware
- Increased use of phone-based Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Each IoT device is a potential entry point for a malicious actor trying to get inside your network. Others can be controlled remotely to extort money from the owner. As more homes and businesses have IoT devices, it’s important for cybersecurity engineers to be prepared and equipped to handle these attacks.
Common roles: Cybersecurity engineer versus cybersecurity analyst
Many people confuse a cybersecurity engineer with a cybersecurity analyst. While both positions join forces to ensure a business’s information security and network resilience, each has a different focus.
The table below summarizes the core similarities and differences between a security engineer and an analyst.
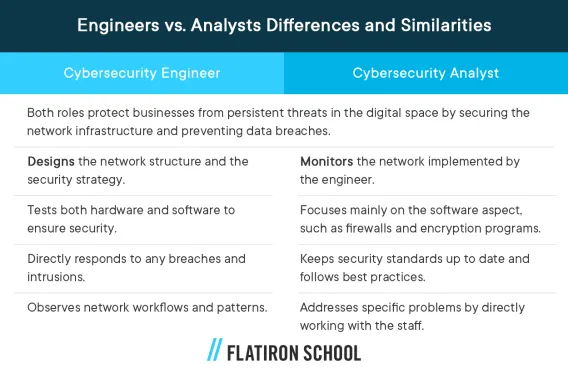
In a larger company, the cybersecurity engineer sometimes oversees a small team with specific tasks designated, including at least one analyst. Meanwhile, the cybersecurity engineer in a smaller company may need to take on multiple roles simultaneously.
Should I become a cybersecurity engineer?
While cybersecurity engineers have significant responsibilities on their shoulders, that’s also why it is one of the most attractive careers in the IT world right now. Especially after the demand created by the COVID-19 pandemic, cybersecurity engineers have become one of the 5 most in-demand cybersecurity jobs of 2020.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics reports a predicted 31% increase in the IT security industry in this decade (2019 to 2029).
Meanwhile, top recruiting and analytics firms, including the reputable Gartner, have all identified a talent shortage in the cybersecurity field. A low supply and an increasing demand means that candidates may have more say in negotiating their salary and benefits. It also means companies will not hesitate to compete for the best talent.
Salary estimate
Of course, another main reason you should consider getting into cybersecurity is the pay and the benefits.

How do I become a cybersecurity engineer?
You have various options when considering learning a new skill. In general, there are three popular ways to learn — college, bootcamp, or self teaching.
Let’s explore each option so you can decide which one is right for you.
1) College
You might be thinking about college because it is the most “formal” and official looking education. It’s true that some employees consider a college degree to be the most trusted credential. However, in cybersecurity, technical ability is typically valued over formal education so don’t count out a bootcamp just yet.
Here are the pros and cons you can expect if you consider attending college for cybersecurity.
Pros of attending college for cybersecurity:
- Highest credibility
- Internship and practical opportunities
- Financial aid options
- Degrees can open more doors
- In-depth curriculum for deeper understanding
- Opportunity to hone managerial & leadership skills
Cons of attending college for cybersecurity:
- Most expensive option due to rising tuition costs
- 2-4 years long before you can start your career
- May require you to live close to campus if there is not an online option
- Curriculum less responsive to industry changes
2) Cybersecurity bootcamp
Are bootcamps worth it? Simply put, cybersecurity bootcamps are for people dedicated to either starting a new career or advancing their knowledge in a short amount of time.
Generally, bootcamps offer intensive, hands-on training to get you job-ready quickly. While some offer flexible pacing options so you can learn on your own schedule, all bootcamps require commitment and the ability to keep up with a fast-moving curriculum.
Therefore, bootcamps are best for those who have time to focus and learn, have a decent budget, and are ready to grow rapidly and aggressively into a new career.
Pros of attending a bootcamp for cybersecurity
- Learn cybersecurity in as little as 15 weeks
- Options to learn on your schedule
- Often provide career service support
- Intensive training focusing on job-ready skills
- Lost of hands-on experience
- Often includes career coaching and a supportive peer community
Cons attending a bootcamp for cybersecurity:
- Some employers may prefer a formal undergraduate or graduate degree
- Can be rigorous and fast-moving
- May need additional self-study
- Credibility can vary, so choose a highly ranked program
- The curriculum won’t be as in-depth as you’d find in college, so additional self-learning may be required to round out your skillset.
3) Self-teaching
For those who aren’t 100% sure if they are ready to jump into a new cyber career, self-teaching is the best approach. It’s the most affordable option among the three learning methods listed here, and it allows you the flexibility to take full control of your schedule. Plus, if you decide you love cyber, you can still choose bootcamp or college to make your training more official.
Here are the pros and cons you should consider when teaching yourself cybersecurity.
Pros of self-teaching cybersecurity
- Self-paced
- Cost-effective
- Focus on only what you want to learn
Cons of self-teaching cybersecurity
- Lack of guidance and support
- Requires self discipline
If you decide to go the self-teaching route, start with a free online cybersecurity workshop.
What skills do I need to become a cybersecurity engineer?
No matter which learning method you choose, you should always start with the hard skills required by a cybersecurity engineer. Some core skills are:
- Programming languages
- Network architecture and maintenance
- Database platforms
- Understanding of various operating systems
Programming languages
Since cybersecurity engineers will plan, design, and implement security measures, it is essential to know not only one, but multiple coding languages to create the most economic, efficient, and resilient solutions.
Some popular development languages are Javascript, JSON, Python, and C++.
Penetration testing
Also known as “pen testing,” penetration testing is a common task for cybersecurity professionals, especially in an entry-level role. When conducting a pen test, the engineer imitates real attacks to test the integrity of current firewalls and other network security mechanisms.
Risk analysis
A cybersecurity engineer needs to oversee the workflow and performance pattern to gather intel on potential risk factors. Sometimes the engineer also participates in the network analyst’s role.
Interpersonal and soft skills
Nonetheless, having hard skills alone won’t make you stand out from the crowd. To remain strong and competitive in today’s talent market, you must equip yourself with soft skills as well.
Some primary soft skills required by cybersecurity professionals are:
- Resilience. Network infrastructure management can be stressful. You need resilience and stress management to maintain your performance level.
- Perseverance. Digging into details and finding needles in haystacks is part of this particular job. While it may be frustrating, you’ll need perseverance to remember your goals and keep going through the challenging parts.
- Problem-solving abilities. Essentially, an engineer’s job is about finding the solutions to existing threats and emerging problems.
- Communication skills. While you primarily work with the network, you still need to know how to effectively communicate with your colleagues and supervisors. After all, you are here to protect them too.
- Curiosity and a learner’s mindset. Cybersecurity is one of the fastest-growing industries. Therefore, you must always be hungry for knowledge to keep yourself on top of your game.
What certifications do I need to become a cybersecurity engineer?
Certifications are an important way to prove your proficiency with or without a degree. In fact, some companies may require you to get a certification even after completing a cybersecurity bootcamp.
Here are a few credible certifications in the cybersecurity world. Keep in mind that each certification has a different focus. So, make sure you’re getting the right one!
CompTIA Security+ Certification
CompTIA Security+ is a global certification validating your baseline skills required to perform core security functions. This is the most fundamental certification for someone considering an IT career.
Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH)
An ethical hacker — also known as a penetration tester — uses white hat methods to mimic attacks on an organization’s network to gain insight into how current implementations of security methods respond. Therefore, a CEH certification is necessary for those wanting to become penetration testers.
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP)
CISSP is the most authoritative certification for cybersecurity, and certified individuals typically earn a much higher salary compared to others. To qualify for a CISSP certification, you must have at least five years of full-time experience in two or more (ISC)² information security domains.
Certified Information Security Manager (CISM)
Flatiron School often recommends the CISM certification because it tests your knowledge in information security governance, information risk management, program development and management, and information security incident management.
Why Learn Cybersecurity Engineering with Flatiron School?
Flatiron School is more than just another cybersecurity bootcamp. We provide you with comprehensive, hands-on training focusing on skills desired by top employers, and will support you through your learning process.
One of the major things that sets us apart is that we offer 1:1 career coaching included in the cost of tuition for 180 days after graduation.
And you can rest assured that you are learning the most in-demand, relevant job skills because our curriculum is regularly reviewed by industry partners. Check out our jobs report for more on hiring stats for how our students perform against the market.
If you’re interested in learning more about a cybersecurity engineering bootcamp, book a 10-minute chat with admissions.
Curious if this course is right for you?
Learn more about cybersecurity engineering
Frequently Asked Questions
Cybersecurity engineering, as a STEM field, is challenging and requires ample dedication. However, nothing is difficult when you have the right path to training. Understand your learning style and hold yourself accountable. That’s how you make steady progress toward your goal.
Yes, indeed. Cybersecurity professionals are heavily sought by various companies, from small startups to large corporations. In fact, in May 2021, there were almost 500,000 cybersecurity job openings in the U.S.
Not all cybersecurity roles require coding, but knowing how to code will definitely give you an advantage in your job search. Check out this article to see which programming languages are recommended for cybersecurity.
A cybersecurity role is critical to a business’s safety and contingency. Therefore, some might find the responsibilities quite stressful. However, if you know your trade, then it’s just like any other job. You shouldn’t worry too much about that.
If you want to get in the field fast, the best choice is to enroll in a credible cybersecurity bootcamp. Alternatively, there are also self-paced learning methods using online courses, training channels, and books.
If you want to get into cybersecurity without an IT background, no problem. A cybersecurity engineering bootcamp is the best path to your new career because you will learn an extensive amount of information about cyber and will get hands-on experience quickly. You do not need a technical background to apply for a cybersecurity bootcamp.
It helps to have a basic understanding of how mathematical equations work, but most math in cyber isn’t done manually. Instead, cybersecurity relies heavily on logical analysis. Additionally, you will also need to learn analytical and statistical skills.




