Key takeaways
-
Cybersecurity bootcamps can be a more affordable alternative to a traditional college degree.
-
Bootcamps provide hands-on experience and learning through real-world projects.
-
Many cybersecurity bootcamps also provide career services to help you find a job after graduation.
-
Flatiron School can help prepare you for interviews, review your resume, connect you with businesses and networks, and help you build your online brand.
-
Many companies look at bootcamp graduates the same as they would a university graduate, academically and experience-wise.
-
Optional industry certifications can help you stand out in your job search.
With the demand for cybersecurity professionals at an all-time high, according to a study done by Tulane University, there is an equal demand for cybersecurity education. Bootcamps are constantly evaluating and evolving their programs to provide valuable information that is highly relevant to the career field.
In today’s job market, bootcamp grads are valued for their technical abilities and often land roles at some of tech’s biggest companies. A college degree is no longer the only way to break into this lucrative industry.
What is a cybersecurity bootcamp?
Cybersecurity bootcamps are intensive, immersive training programs designed to prepare you for entry-level cybersecurity jobs. Bootcamps are much shorter than going back to college for four years.
In some cases, you can complete a cybersecurity bootcamp in as little as 15 weeks. There are also flexible programs where you can choose the pace you want to learn and complete the program in 20, 40, or 60 weeks.
Cybersecurity bootcamps offer hands-on training and projects that mimic what you will experience in a job. It’s an efficient way to learn the technical, strategic, and analytical skills you need to get a job and start a successful career in cybersecurity.
What will I learn in a cybersecurity bootcamp?
There are many topics that you will learn in a cybersecurity bootcamp —generally, the topics depend on the bootcamp itself. Cybersecurity bootcamps teach you the foundational skills you need to begin protecting computer systems and networks from cyberthreats.
During the fundamentals, students gain insight on why cybersecurity is vital in the tech world, and they will learn more about the integral role of cybersecurity professionals. In some cybersecurity bootcamps, you will also learn the beginnings of ethical hacking.
For many in IT, this is an exciting role because they are getting an opportunity to take down the firewalls and infrastructure of a website, platform, or an app, and they get compensated fairly well for it—there are also no threats of being arrested, as this is a safe and legal procedure.

You will also learn security operations in a cybersecurity bootcamp. Topics within security operations include:
-
Preventing cyber attacks
-
Detecting threats
-
Assessing cyber incidents
-
Responding to cybersecurity threats, incidents, and hacks
-
Documenting and reporting on cybersecurity incidents and potential threats
As opposed to a 2-4 year college, bootcamps offer hands-on, real world application, and a more streamlined timeline — tending to range between 3 months to 9 months, according to CyberDegrees.
If you are interested in a cybersecurity engineering bootcamp, it does help to have previous experience in IT or an interest in computers since these are fairly technical roles. Whether you have previous experience or not, you should be prepared to learn at a fast pace.
Finally, you should choose a bootcamp that has experienced instructors. Learning from instructors that have experience in the field will help you understand exactly what you will be doing in your day-to-day role. Your instructors should also be experienced educators and effective, passionate teachers.
Will cybersecurity bootcamps help you land a job?
Cybersecurity bootcamps aren’t just there for educational and experience requirements—often, cybersecurity bootcamps will offer career services to help you land a job in your desired field.
For example, Flatiron School offers 180 days of 1:1 career coaching after graduation. In many cases, cybersecurity bootcamps have connections with big companies, which can help streamline your process to finding a full-time position in cybersecurity.
Another benefit of bootcamp is being able to build your professional network. Often, cybersecurity bootcamps will bring in industry speakers and alumni so you can make connections at companies within the area. In addition, you can learn what it’s like to work in a full-time cybersecurity role from these speakers.
If you worked in IT before bootcamp, you may qualify for higher-level positions within cybersecurity. Otherwise, most bootcamp grads start in entry-level positions as cybersecurity professionals.
How long does it take to get a job after a cybersecurity bootcamp?
The answer is up to you and how much effort you put into your job search. While some bootcamps offer career coaching, they aren’t going to give you a job. You still have to follow the guidance of the career coach and work hard to find and apply for jobs.
The good news is that a cybersecurity bootcamp is much shorter than going back to college. In some cases, you can finish a cybersecurity bootcamp in as little as 15 weeks — as opposed to 2 or 4 years of college — and then be on your way to your new career quickly.
Once you finish bootcamp, the time to find a job can vary. For some people, they can land a job before they even graduate, and for others, it could take several months.
Every cybersecurity bootcamp has its advantages. For example, some bootcamps offer 1:1 career coaching for 180 days after graduation to support you in the job search.
At Flatiron School, they offer many helpful services to their students to ensure that the process and transition from an experience-based educational setting to a job or a career is smooth.
Do companies hire bootcamp graduates?

Bootcamp aren’t the same as an undergraduate college degree or a Master’s degree, but it doesn’t decrease your chances of landing a job—in fact, according to this research done by Indeed, 72% of employers think that bootcamp graduates have just as much preparedness and educational requirements as candidates with computer science degrees.
Companies love hiring bootcamp graduates, whether they’re small startups, non-tech companies, or tech giants. Some of the big companies that are known for hiring bootcamp graduates are:
Flatiron School graduates have gone on to work in many companies, including Kickstarter, The New York Times, LinkedIn, Yahoo!, Facebook, and BuzzFeed. No matter where you look, more companies are joining the tech giants by hiring bootcamp graduates.
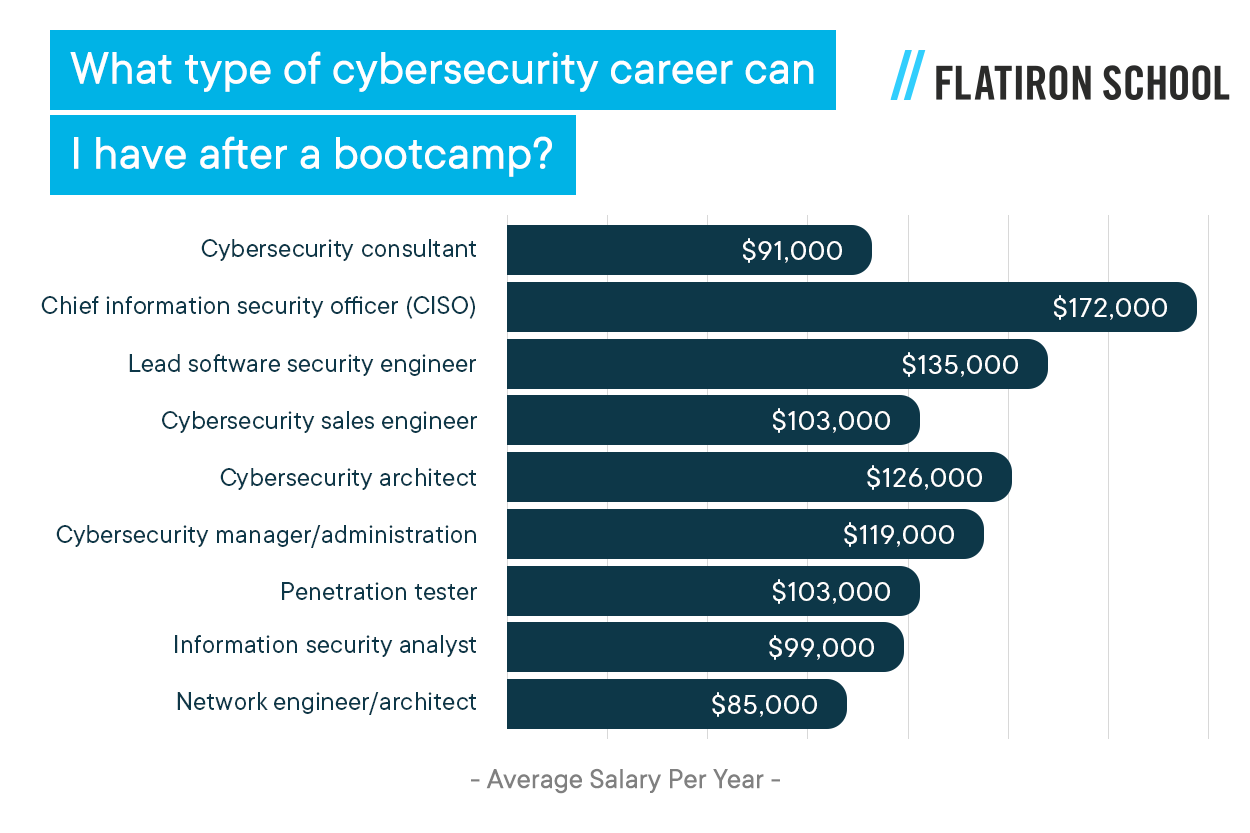
What type of cybersecurity career can I have after a bootcamp?
Here’s a small list of the most common roles within cybersecurity and their average salary (current as of May 2021):
Cybersecurity consultant
Cybersecurity consultants play as both the attacker and the defender in computer systems, networks, and software programs.
Average Salary: $91,000 Per Year
Lead software security engineer
Lead software security engineers coordinate with systems administrators, program management, and validation engineers on security-related activities and requirements.
Average Salary: $135,000 Per Year
Cybersecurity sales engineer
Cybersecurity sales engineers contribute to sales through pre-sale/post-sales technical consulting activities through switches, routers, and network security.
Average Salary: $103,000 Per Year
Cybersecurity architect
Cybersecurity architects are responsible for planning, testing, implementing, and maintaining an organization’s computer and network security infrastructure.
Average Salary: $126,000 Per Year
Cybersecurity manager/administration
Cybersecurity managers monitor the channels through which information flows into and out of an organization's information network (email, routers, etc.).
Average Salary: $119,000 Per Year
Penetration tester
Penetration testers act as a certified ethical hacker that attempts to cyberattack a computer system and evaluate its security protocols.
Average Salary: $103,000 Per Year
Information security analyst
Information security analysts work to secure information networks and systems in many different types of organizations.
Average Salary: $99,000 Per Year
Network engineer/architect
Network engineers develop and implement computer network systems for small or large companies.
Average Salary): $85,000 Per Year
Can you get a job with a cybersecurity certificate?
Industry certifications are optional and allow you to validate knowledge of best practices in specific areas of cybersecurity.
There are literally hundreds of certifications available, from general to vendor-specific, entry-level to advanced.
In many cases, even after you finish cybersecurity bootcamp, your next step will be to complete an industry certification.
Which certifications should I get after I graduate from a bootcamp?
There are different certifications that will help your chances of landing a job in a specific sector of your desired field.
Here are some specific certifications for cybersecurity positions:
-
If you want to become a cybersecurity analyst, get CompTIA’s Cybersecurity Analyst (CySA+)
-
If you want to become a cybersecurity engineer, become a Systems Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP)
-
If you want to become a penetration tester, get EC-Council's Certified Ethical Hacker Certification
-
If you want to become a cybersecurity threat analyst, get CompTIA’s Security+
-
If you want to become a cybersecurity consultant, become a Systems Security Certified Practitioner (SSCP)
Summary
In summary, cybersecurity bootcamp is an excellent way to be prepared for the workforce. But, to get a job, it’s up to you. A bootcamp will adequately prepare you for a job, but it won’t give you a job. You still need to put in the work to find and apply for jobs. But you won’t be on your own. Your bootcamp career coach will help guide you through the process.
Ready to start a bootcamp? Apply now for cybersecurity engineering at Flatiron School or schedule a 10-minute chat with the admissions team to learn more.




