
Data Science for beginners
The popularity of data science in recent job reports may have left you wondering what all the fuss is about. After all, what is data science?
At its heart, data science is the study of information. Most companies use it to help make business decisions, solve complex problems, and create strategies to improve results and performance. From understanding water use and air quality to create a more sustainable society to helping insurance companies mitigate risk, data science is important to every industry.
The data science field is evolving and continues to grow (fast) as the amount of data generated and collected across the globe increases. Every industry — from retail to social media to advertising and space travel — uses data science to make smart, data-driven decisions.
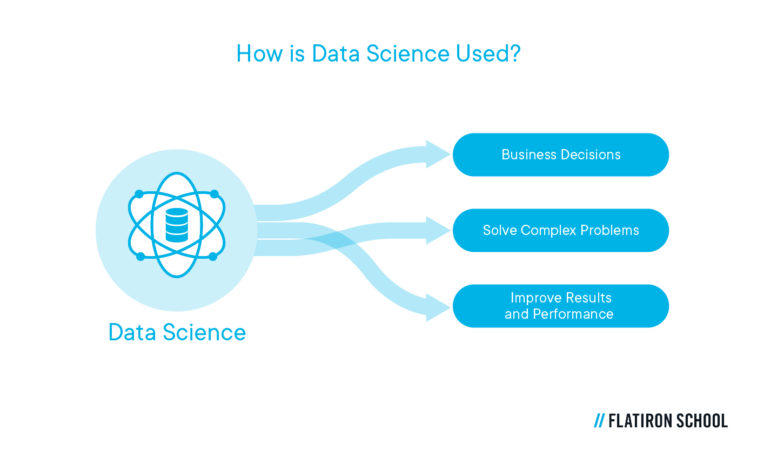
How is data science used?
Data science deals with the enormous volumes of data that are generated from business operations, medical research, and nearly every other endeavor. Companies even track consumer’s actions from various websites and add that information to data sets to make decisions.
Businesses and corporations are drowning in data. They want to use this data to unlock insights and drive growth.
Data science uses complex machine learning algorithms to build predictive models, making it more predictive and less prescriptive than data analysis. It blends tools, algorithms, and machine learning principles to uncover patterns from raw data and visualize them for non-technical audiences.
Data Science is the cornerstone of artificial intelligence (AI), with subsets of AI including deep learning and machine learning.
Deep learning analyzes videos, images, and unstructured data in ways machine learning cannot. Machine learning is more about computers that can think and act with less human intervention. AI encompasses all of this and attempts to make machines think and act more like humans.
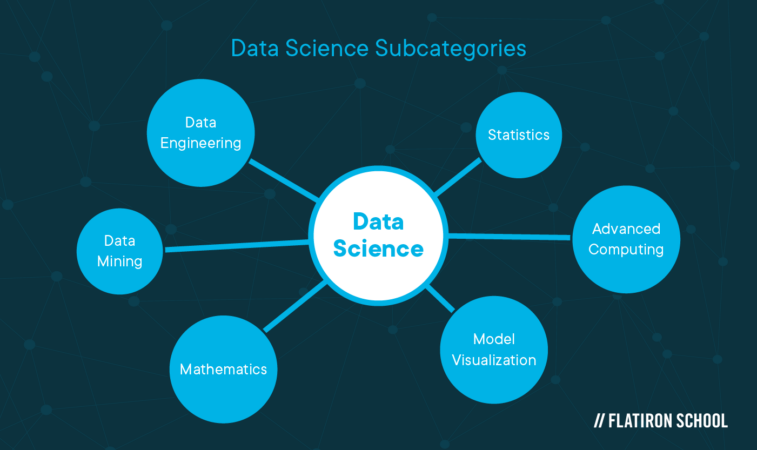
Data science subcategories
- Data engineering
- Data mining
- Mathematics
- Statistics
- Advanced computing
- Model visualization
Data science collects your actions, organizes them with your other activities and those of others, looks for patterns, and creates an output, like a recommendation, based on the data.
How is data science changing the world?
Better decisions lead to a better world. Data science can improve decision-making processes in business, medicine, science, and almost every other field or industry. It helps uncover patterns and provides predictive analysis.
From preventing blindness and treating drug and alcohol addiction to fighting poverty, data science is being utilized not only as a business tool – but for the greater good of society.
The world already uses data science to predict disruptions in travel and optimize the airline industry. It’s used for decisions in retail, like furniture shopping, and streamlines treatment discovery in medicine. For instance, Project Warp Speed would not have been possible without data science.
If you want a career where you can use your analytical skills to change the world, this field can lead to a lucrative career with vast employment and career growth opportunities. Demand continues to rise, and the average pay in the U.S. is around $115,000* annually.
Is data science a good career?
Data science is considered one of the best job categories in the U.S. They have a high median base salary, and the employee satisfaction rate is significantly positive.
What are average data science salaries?
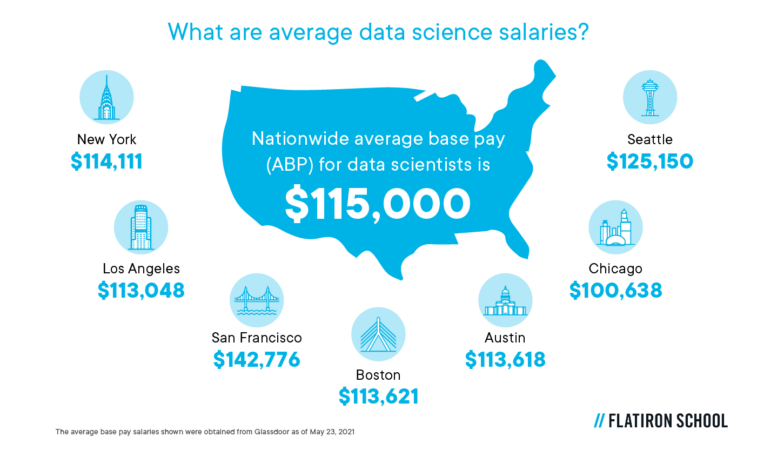
The average base pay salaries shown were obtained from Glassdoor as of May 23, 2021:
- Nationwide average base pay (ABP) for data scientists is $115,000*
- New York — $114,111
- Los Angeles — $113,048
- San Francisco — $142,776
- Boston — $113,621
- Austin, TX — $113,618
- Chicago — $100,638
- Seattle — $125,150
The salary differentials across the country may reflect both the cost of living and demand.
What does a data scientist do?
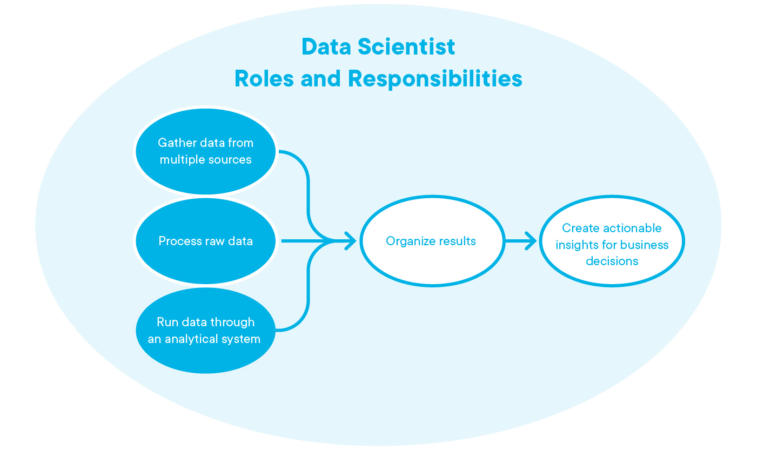
The central role of a data scientist is to answer the right questions and present easily digested results to stakeholders.
Roles and responsibilities of a data scientist include:
- Gather data from multiple sources
- Process the raw data
- Run data through an analytical system using algorithms based on machine learning or statistical models
- Organize the results & create actionable insights for business decisions
For example, data science results can profoundly impact medicine and security by doing things like predicting the best new diabetes treatment or identifying and thwarting national security threats.
Data science professionals have skills in computer science, data modeling, statistics, and math. Also, they have a grasp of business that guides them in answering significant questions that help organizations make objective decisions.
What skills do I need for data science?
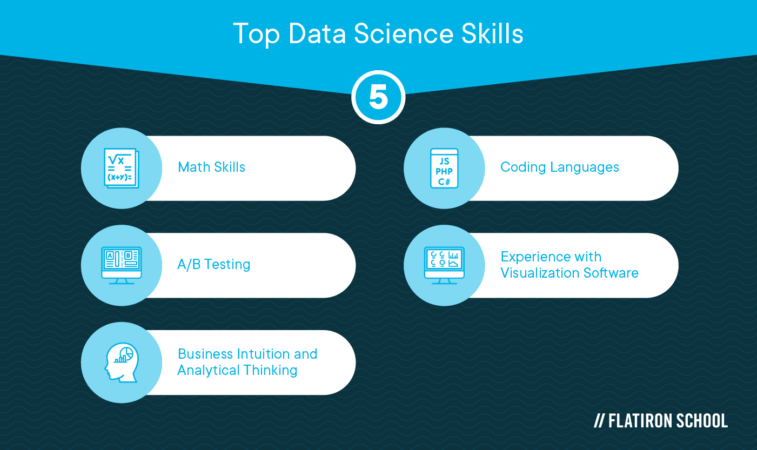
Excellent math skills are required in a data scientist’s toolkit, but obtaining these skills may not be as arduous as you think.
For example, calculus is a requirement in data science. However, understanding how its principles and applications affect data models is more important than the ability to calculate derivatives. It’s more like understanding how calculus works rather than doing calculus.
Other essential math skills include:
- Linear algebra, primarily how to solve a variable, which is handy in coding and other tasks
- Statistics and probability, which are more important than calculus and linear algebra
Statistics and probability are the primary workhorses of data science. You need a firm grasp of statistics, but you don’t need a degree in the area. You will probably learn more through trial and error and as you gain experience in your particular industry.
Data science skills encompass data visualization and warehousing, along with processing. Depending on their role, data scientists become expert coders in languages such as R and Python.
The areas of visualization and warehousing require knowledge of Tableau, Cognos, RAW, Apache Spark, AWS Redshift, and ETL as part of a toolkit to enhance data gathering, analysis, and graphical presentation. Statistical analysis, computer science, programming, data storytelling, and machine learning are all part of the skill set.
Other skills include A/B testing, which is the process of showing two types of the same web page to different audiences simultaneously to see which earns more conversions or interactions. Another is linear regression, which is used to see how close data points line up with the best fit line. This function compares the data points with each other to visualize the trend, determining where it’s headed or how it’s changing.
In addition to technical skills, data scientists also need soft skills, such as domain knowledge, business intuition, analytical thinking, curiosity, critical thinking, and interpersonal skills. You won’t be sitting in a cubicle crunching numbers all day. You’ll need to be able to talk about the implications of the data points with people who are not data scientists.
What programming languages do data scientists use?
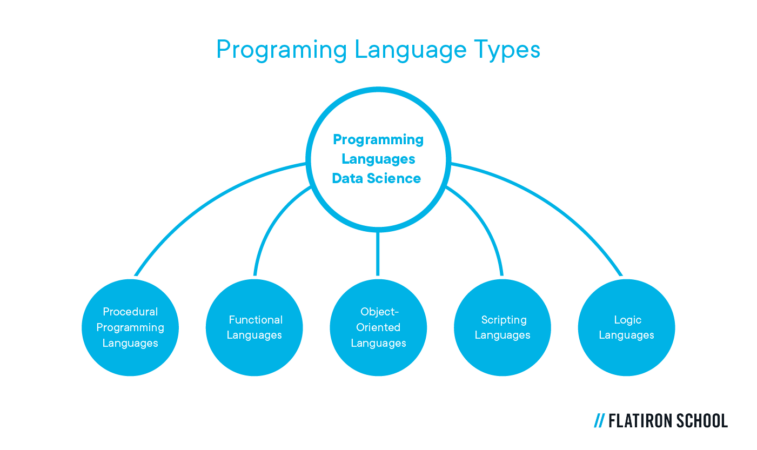
Programming and coding skills are critical in data science. Different types of problems require particular software solutions to answer them. Programming languages are used to write lines of code to make up a computer program. Lines of code are digital instructions, commands, and syntax translated into digital output.
There are five main types of programming languages, each serving different functions and with specific advantages and disadvantages.
The 5 main types of programming languages include:
- Procedural programming languages
- Functional languages
- Object-oriented languages
- Scripting languages
- Logic languages

Of the existing data science programming languages, data scientists often use one or more of the following, with Python being the most popular and used:
- Python
- Javascript
- Java
- R
- C/C++
- SQL
- Scala
- Julia
- SAS
- MATLAB
Deciding which language to learn depends on what you want to accomplish. Different tasks require different levels of knowledge, and one language may be more suitable than another to answer the question you have.
Consider, also, the expertise you may already have in a language. You may wish to become stronger in that language or select one that complements it. The scale at which your organization uses data science also helps determine the language used.
What are the roles and responsibilities of a data scientist?
What does a data scientist do? They design data modeling processes and create algorithms & predictive models. They extract data the business needs and help analyze it so they can share insights with their peers.
Data scientists also work with stakeholders on framing the business problem. They need to understand the stakeholders’ goals and determine how data can be used to achieve them.
Their primary role is to adjust existing statistical and mathematical models to acquire data and make discoveries. They turn formal business problems into data questions to create data-driven answers. Using data visualization, they communicate the findings and their implications to less-technical team members and stakeholders.
What are common data scientist job titles?
Job titles may change in response to business or industry needs. However, the preparation for those roles remains rooted in data science. The following are some example career titles in data science:
Data Scientist:
- Data scientists use math and programming skills to analyze data sets for insights that might benefit their organization.
Data Analyst:
- Data analysts translate data into an accessible format for companies to give them a snapshot of their current performance. Business leaders use their input to make tactical decisions about their organization’s future direction.
Data engineer:
- Data engineers look for trends in large data sets. They also build algorithms that help organizations mine useful information from raw data.
Statistician:
- Statisticians use different statistical models and methods to analyze real-world issues and interpret the data. Companies use their input as part of their decision-making process.
Machine learning engineer:
- Machine learning engineers create and run automated software programs capable of building predictive models from large data sets. The programs “learn” from the information collected, helping them develop more accurate predictive models.
Business intelligence developer:
- Business intelligence developers leverage software tools to manipulate data into a format that’s understandable for non-technical users. Companies use this to get a sense of the current state of their business.
Read more about these high-paying data science jobs and how to get them.
What is the difference between a data analyst and data scientist?
Data analysts & data scientists tend to be people with an investigative mind, super curious, and enjoy trying to solve a puzzle. They are looking for trends that piece together and tell a story. Ultimately, they are storytellers.
Also, they tend to be very patient and observant because the solution or the very next step isn’t always obvious. Finally, they blend logical and creative thinking very well.
The roles of data analysts and data scientists are often used interchangeably. However, they have very different responsibilities.
A data analyst’s primary role is to scan and analyze data, where a data scientist collects, cleans, and explains the data. An easy way to think of it is that an analyst is often more of a beginner role, and a data scientist may have more experience or more advanced education.
What does a data analyst do?
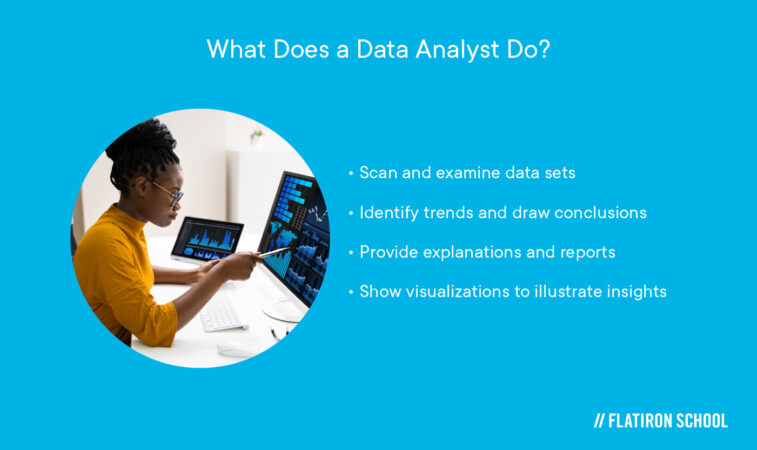
Data analysts oversee a company’s data.
They scan and examine (analyze) data sets to identify trends and draw conclusions. They provide explanations and reports and show visualizations to illustrate insights. Data analysts are proficient in SQL and business intelligence software, which they use to interpret structured data and analyze the trends and patterns therein.
They use tools like Tableau and Excel to maintain a metrics dashboard, and their role has been around for decades.
However, data analysts do not need to be expert programmers. Their expertise is more in the realm of analytics and data management. For instance, they can generate marketing reports and future sales projections and show the success of ad campaigns.
To become a data analyst, you need to learn how to interpret trends from historical data, prepare summary reports, Information management, data cleansing, data mining, developing data pipelines.
Further reading: What is data analytics?
What does a data scientist do?

Data scientists are often considered to be more senior than data analysts, and they tend to be paid more. A data scientist collects, cleans, and explains the data. Their primary role is to adjust statistical and mathematical models and apply them to the data.
Data scientists are responsible for translating formal business problems into workable data questions. They build predictive models for upcoming data and can theorize, implement, and acquire data effectively.
Data scientists can get quite creative when displaying information and discovering ways to make their findings more transparent and compelling.
In short, they can interpret data like data analysts, but also code models or algorithms to gain more insight into the data. Data analysts act more like translators while data scientists act in a hybrid capacity, helping companies turn data into practical and actionable information through coding.
What is the difference between business intelligence and data science?
Business intelligence (BI) focuses on using data housed by analysts to find problems and solutions.
BI analysts examine previous data for hindsight and insight to describe business trends. BI analysts take data from external and internal sources, prepare it, run queries on it, and create dashboards for activities like quarterly reviews or solving business problems. Sometimes BI can evaluate the impact of particular events on the near future.
Data science looks forward, not back. It is exploratory, intending to make informed decisions. It answers open-ended questions as to what and how events occur.
In other words, data science is a strategic role focusing on using information discovered by a data analyst to identify problems and find solutions.
How can I become a data scientist?
There are three paths to become a data scientist — through self-study, college, or bootcamps.
You do not need a four-year degree to become a data scientist. However, you do need a lot of knowledge in the field, especially in big data and mathematics. Also, it’s beneficial to learn one or more programming languages. Python is often the first language that many data scientists learn in a bootcamp.
If you’re thinking “Yes, I love this field! I want to start my new career right away!” a data science bootcamp is an excellent path to get the skills you need in the shortest amount of time possible. Some programs can be completed in as little as 15 weeks.
Plus, the curriculum in a data science bootcamp is often created specifically for hands-on, job-ready portfolio skills. You can make a big difference in the world with your data science skills, and a bootcamp will get you there.

The three paths to becoming a data scientist:
1. Teach yourself data science
Self-study or self-teaching is difficult and requires immense self-discipline. You need to research thoroughly to ensure you are learning the right skills. Since the field changes quickly, you need to put some checkpoints in place along your way to reassess your learning.
There are plenty of books and online resources dedicated to the field, as well as videos and even free lessons online. The good thing about self-teaching is there is little to no cost, and you can go at your own pace. You can slow down when you need to, and you can select materials from multiple sources, which reduces bias.
On the other hand, it’s hard to stick with it. There are no career services or support. It’s difficult to determine if you are studying the right material, plus you have nobody to ask for advice. Worst of all, some hiring managers do not see self-education as valid, and you may not have a portfolio to show in interviews.
2. Go to college for data science
Many job descriptions do ask for advanced degrees, so you might consider going to college for data science. Most successful data science bootcamps students have at least a bachelor’s degree.
However, if you already have a college degree, “going back to school” may not be your most comfortable choice. See if your employer is willing to pay for it or you qualify for assistance since a four-year degree can cost upwards of $99,000 depending on the type of college or university you choose.
3. Enroll in a data science bootcamp
Data science bootcamps, on the other hand, teach skills necessary to succeed in the field without any of the “fluff” core curriculum.
Some bootcamps work with employers and hiring companies to continually review their curriculum and ensure it is up-to-date with current industry trends and skill set requirements. This is also a great option for someone who is interested in quickly changing their career path since you can complete some programs in as little as 15 weeks.
The cost of a data science bootcamp can run from $5,000 to $20,000, and it may last from a few weeks to six months or more. One perk of a bootcamp is that you come away with a portfolio of projects to share with prospective employers and hiring managers.
Another benefit of a bootcamp is that the career coaching can be more intensive than what you get with traditional college. For example, some programs offer 1:1 career coaching for 180 days after graduation to help support you through the job search process.
Benefits of data science bootcamps
Many bootcamps have career services and job search assistance included in the cost of tuition. Bootcamp providers know the latest employer needs, and hiring managers tend to favor bootcamp graduates over self-taught applicants. Also, you have the chance to connect with other aspiring data professionals.
While data science bootcamps have upfront costs and the course is intense, you ultimately learn what employers are looking for and gain hands-on skills that are directly applicable to the job market. It provides the discipline for learning and working through the course of study while providing support for students and graduates.
Additionally, a bootcamp has a less philosophical outlook on data science — meaning, instead of learning the “big picture” of data science, you are learning in an environment meant to replicate the workplace. With an emphasis on practical education and skill-building, bootcamps are pretty fast-paced, but you have support from teachers, other students, and online forums to help you out.
You may still run across a hiring manager that prefers a degree over a bootcamp, but that may help you decide between employers. In fact, many hiring managers say that bootcamp grads are just as prepared as candidates with traditional 4 year degrees.
Make a career change
Humanity has gone from handing down knowledge in stories to gathering data points from everything that occurs throughout the world. Data science is there to make sense of it and help organizations make data-driven decisions as they grow and move forward.
Overall, a career in data science can be rewarding and lucrative. Employment opportunities are unlikely to lose steam anytime soon.
Still curious if data science is for you? Try a free lesson or book a 10-minute chat with admissions.
Curious if data science is right for you?
Frequently Asked Questions
Data science deals with large volumes of data. A data scientist will sort and analyze this data to answer complex questions in business and other fields. Data science uses computer coding and mathematics to examine and visualize data.
Data science courses include programming languages such as Python and R. You learn about data structures, relational databases, and how to handle structured and unstructured data. You also learn to visualize data.
There are even free data science tutorials that you can try before jumping into a bootcamp.
The national average base pay for data scientists is $115,000 as of May 2021, according to Glassdoor.com.
Data science helps make sense of the world around us through analyzing and visualizing data. Every industry needs data scientists to help them make data-driven decisions and plan for the future.
Data science helps make sense of a world filled with data. Every organization has a well of data they need to examine to answer questions and improve processes. Ad hoc decisions rarely turn out well, and data science is the foundation of data-driven decision-making.
The best data science certification is the one that interests you the most. Data scientists work in every industry and use a wide variety of skills. Indeed lists 18 certifications you can earn, each fitting into a particular area.
To become a data scientist, you need a good grounding in the principles of calculus, especially the areas affecting data modeling. You also need to know linear algebra, probability, and statistics. Other data science math areas include discrete mathematics, graph theory, and information theory.
*this number is current in June 2021






